Mediocrity drift
Mediocrity drift
/ˌmiːdɪˈɒkrɪti drɪft/ (n.)
|
The Human Resources military-industrial complex
|
“The bank emphasizes that staff will also be reduced through natural attrition, not filling vacant positions or offering early retirement.”
- — Credit Suisse Job Cuts are Causing Unrest, finews.com, December 2022
A curious, unintended, negative feedback loop of lazy human capital management. If you don’t proactively retain good staff, and if you don’t actively manage out poor staff — if you manage by tactical hiring and “natural attrition” — the general quality of your staff relative to their cost will decline.
This is a logical consequence of this style of management, at least if you accept four general assumptions:
Good staff leave by themselves: Staff with the gumption to leave tend to be relatively good employees, relative to what you pay them. These people are, therefore, underpaid. No surprise: that’s why they’re leaving.
Bad staff don’t: Conversely, those who are already overpaid for what they do tend not to quit, because they know are already onto a good thing. These staff may leave, but only to join an employer even more gullible that you. Otherwise, they won’t leave unless you make them, by performance management or through a RIF. These people, therefore, are generally overpaid. That’s why they stay.
You have to pay lateral hires the market rate: When you replace leavers, you have to pay the market rate. If the person leaving was underpaid relative to the market, you have two choices: pay more for her replacement, or hire a less experienced replacement. Either way, you are getting someone who is paid at their own cost-value threshold.
Subgroups are normally distributed: That the equilibrium value of your personnel is normally distributed around the cost-value threshold, and so is that of each subgroup of your personnel however chosen. So, you will have as many good staff as you do bad ones. And you’ll have as many good compliance staff as you do bad ones, and as many good left-handers as bad ones, and young, old, men, women and so on. Each such group will within their own group have broadly similar distributions of outperformers and plodders. (This is simply assuming that the law of averages applies).
Now we can see a negative feedback loop here. If all people you hire have an equal chance of working out well — their relative competence is evenly distributed — and those who outperform are likely to quit while those who disappoint are likely to stay, over time, the competency of your workforce will skew mediocre.
Call this “mediocrity drift”.
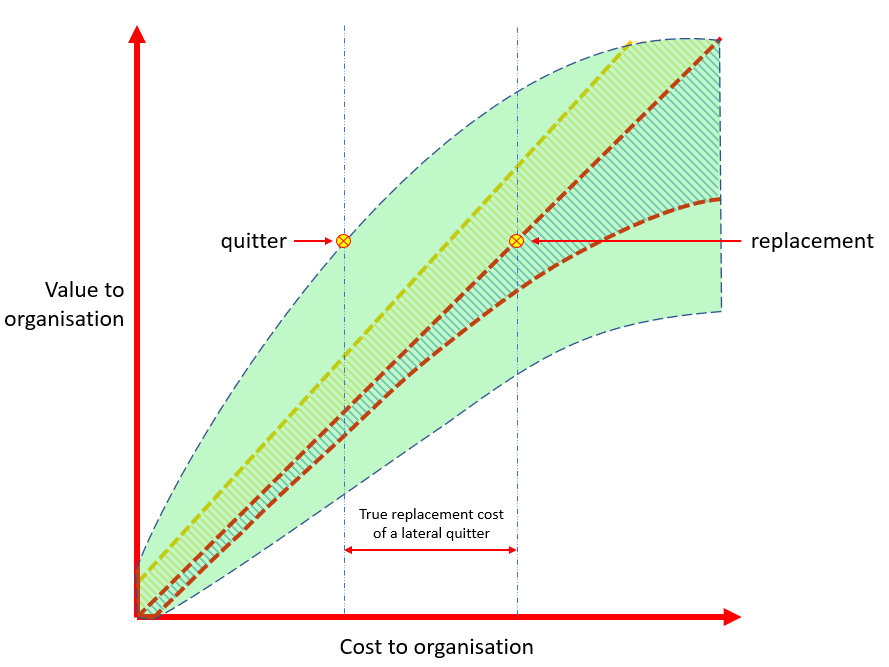
Outperforming quitters will be replaced — at necessarily greater cost, ceteris paribus, because the one and only time you are obliged to mark to market is when you hire — by those having no institutional knowledge, no internal network, and even controlling for that, only an “evens” chance of working out well.
System effects
Here is systemantics in its natural state. How incoming lateral hires perform will remain to be seen but, remember, performance is measured relative to cost. One firm’s incoming lateral hire is another firm’s lateral quitter. An outperforming lateral quitter marks herself to market, gets a pay-rise (why else leave?) and enters her new firm at the cost-value threshold. When she pitches up, she is no longer an outperformer. True, she may turn out that way, but it is not certain. She is just as likely — presuming a normal distribution again — to underperform.
Secondly, notice how pernicious the idea of the average is here.
Affirmative action bummer
If so, then a system which favours one group (group A) over another (group B) has a counterintuitive effect on the remaining populations of both groups: on average, the unfavoured group will increase in relative value, and the favoured group will decrease in relative value, even though no individual performance, in either group, changes at all.
On average, the group A is paid progressively less. It looks like group A members are being systematically discriminated against on pay, but this is not so (in this model, no-one’s pay changes) in fact group A members are being favoured for poor performance.
On a second glance, you can see why this should be so. The process systematically weeds out underperforming members of group B and overperforming members of group A. The “good” side of the distribution will progressively become group B-dominated — they are not being bid away as frequently — and the “below par” section will becomes progressively group A dominated, as poor performing group B members are selected for eradication.