Contractual negligence: Difference between revisions
Amwelladmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Amwelladmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==={{tag|Fraud}}=== | ==={{tag|Fraud}}=== | ||
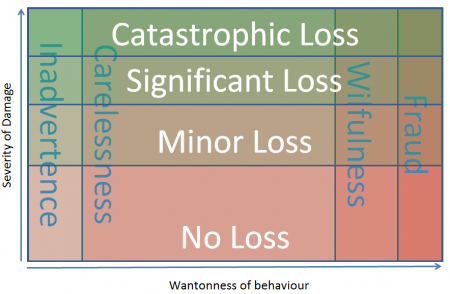
[[File:Contractual loss.PNG| | [[File:Contractual loss.PNG|450px|thumb|right|Damage against Wantonness. Mapped.]] | ||
You can't exclude contractual liability for fraud, so it's hardly a great concession to say so in a contract. | You can't exclude contractual liability for fraud, so it's hardly a great concession to say so in a contract. | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 29 April 2016
An attorney eyes you wistfully and slides a draft across the table to you. It states: "Party A shall not be liable for any losses, howsoever caused, unless they arise directly from its own negligence, fraud or willful default".
What is one to make of this? At a glance it seems perfectly reasonable. To be sure, it is time-honoured boilerplate, thrown into contracts to close them out like chump change tossed into the bill plate at the end of an agreeable meal. But it doesn't make a lot of sense. Let's do the easy ones first.
Fraud
You can't exclude contractual liability for fraud, so it's hardly a great concession to say so in a contract.
Wilful Default
A heartily-bandied phrase which sounds like it ought to mean something specific. The best guess of this fellow is it means a "deliberate refusal to perform one's obligations under a contract": not too far removed from fraud (it raises a presumption of fraudulence on the part of the actor in agreeing to the obligation in the first place) but in any weather a subset of the class of events called "breaches of contract".
Breaches of Ccontract, QED, entitle an innocent party to redress under the law of contract. So it ought cause your heart to leap to find a counterparty offering to be responsible for flagrant examples of this type of behaviour. Indeed; you might wonder why less wilful "defaults" aren't captured.
For here's the point, lazengem: The point of a contractual obligation is to have some means of enforcing its performance or achieving compensation for its non-performance. Is that what negligence is meant to do?