Playbook: Difference between revisions
Amwelladmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Amwelladmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{A|negotiation| | {{A|negotiation| | ||
{{Image| | {{Image|how playbooks work|png|A [[playbook]] yesterday.}} | ||
}}{{d|{{PAGENAME}}|/ˈpleɪbʊk/|n}} | }}{{quote|“Make your documents better. Stop wasting everyone’s time — including your own — with pantomimes.”}} | ||
{{d|{{PAGENAME}}|/ˈpleɪbʊk/|n}} | |||
A comprehensive set of guidelines, policies, rules and fall-backs for the [[legal]] and [[credit]] terms of a {{t|contract}} that you can hand to the itinerant [[school-leaver from Bucharest]] to whom you have off-shored your [[master agreement]] {{t|negotiation}}s. | A comprehensive set of guidelines, policies, rules and fall-backs for the [[legal]] and [[credit]] terms of a {{t|contract}} that you can hand to the itinerant [[school-leaver from Bucharest]] to whom you have off-shored your [[master agreement]] {{t|negotiation}}s. | ||
She will need it because | She will need it because otherwise she won’t have the first clue what do to should customers object, as they certainly will, to the preposterous terms your [[risk controller|risk]] team has insisted go in the first draft of your {{t|contract}}<nowiki/>s. | ||
A well-formed playbook ought, therefore, to be like assembly instructions for an Ikea bookshelf. | |||
But Ikea bookshelves do not answer back. | |||
=== Triage === | |||
As far as they go, playbooks speak to the belief that ''the main [[risk]] lies in not following the rules.'' | |||
They are of a piece with the [[doctrine of precedent]]: go, until you run out of road, then stop and appeal to a higher authority. By [[Triage|triaging]] the onboarding process into “a large, easy, boring bit” — which, in most cases, will be all of it — and “a small, difficult, interesting bit”, playbooks aspire to “solve” that large, easy, boring bit by handing it off to [[Proverbial school-leaver from Bucharest|a school-leaver from Bucharest]]. | |||
Doing large, easy, boring things should not, Q.E.D., need an expensive expert: just someone who is not easily bored, can competently follow instructions and, if she runs out, knows who to ask. She thus tends tilled, tended and fenced land: boundaries have been drawn, tolerances set, parameters fixed, risks codified and processes fully understood. Our children may safely gambol in these fields, where nothing perfidious can befall them. | |||
Playbooks maximise efficiency when operating within a fully understood environment. | === Escalation === | ||
Playbooks maximise efficiency when operating within a fully understood environment. None will ever say, “if the customer does not agree, ''do what you think is best''.” Instead, they will say things like, “any deviations must be [[Escalation|escalated]] for approval by [[litigation]] [[and/or]] a [[Credit]] officer of at least C3 rank”, | |||
The idea is to set up a positive feedback loop such that, through anecdotal [[escalation]], concerned [[control function|risk control groups]] can further develop the playbook to keep up with the times and deal with novel situations, the same way the [[common law]] courts [[Doctrine of precedent|have done since time immemorial]]. The playbook is a living document.<ref>This rarely happens in practice. [[Control function]]s make ''[[ad hoc]]'' exceptions to the process, do not build them into the playbook as standard rules, meaning that the [[playbook]] has a natural sogginess (and therefore inefficiency).</ref> | |||
In practice, this does not happen because no-one has any time or patience for playbooks. | |||
===Example=== | |||
For example, illustrated in the panel above: | |||
:A playbook stipulates starting position ''X'', but allows that if a customer of type B does not agree to ''X'', a satisfactory compromise may be found at ''Y''. | |||
:The playbook “empowers” the negotiator to offer ''Y'' — some way yet from any sort of reasonable market standard — without further permission. | |||
:Should customer B not agree to ''Y'', there must be an [[escalation]], to a junior risk officer, who may sanction a further derogation to ''Z —'' still unnecessarily conservative, but no longer laugh-out loud preposterous. The negotiator trots back to the customer with ''Z''. | |||
:Should customer not accept ''Z'' either, there will follow an extended firefight between risk personnel from either organisation — conducted through their uncomprehending negotiation personnel — taking the negotiation through ''Z''', which will culminate with escalation to sales who might optimistically suggest ''N'', and if that doesn’t do the trick, [[senior relationship management]] will be wheeled in, and will cave instantly to the client’s demand to reach a craven surrender at position ''Q'', some way ''past'' the market standard and anything remotely necessary or reasonable. | |||
By codifying this process, so the argument goes, not only may we engage materially cheaper negotiation personnel, but we can triage our clients and improve our systems and controls. | |||
But ''really''. | |||
=== Design and user experience === | |||
We have certainly ''added to'' our systems and controls; no doubt about that. | |||
But only positions ''X'' through ''Y'' are codified in the playbook. All those wonderful systems and controls were in play only between ''X'' and ''Y'' which turned out, ''quelle surprise'', to be a mile behind the front line. | |||
No doubt middle-management can regale its superiors with assorted [[Gantt chart|Gantt charts]], [[dashboard]]s and verdant [[traffic lights]] attesting to how well the [[documentation unit]] is operating. But all these gears are engaged, and all the systems and controls are running, ''over the easy, boring bit'' ''of the process''. | |||
And, at a cost: following this byzantine process to gather this data occupies people and takes time: ''all'' negotiations take longer, and none of these gears, rules and triage are engaged at any point where the data might be interesting: the exceptions. | |||
The conundrum: since we know our walk-away position is Z (and, at a push, Q) ''why are we starting at X''? ''Why is there a fall-back to Y?'' | |||
Why mechanise an area of the battlefield behind your opponent’s lines, which you know you have no realistic expectation of occupying? | |||
=== Form and substance === | === Form and substance === | ||
When it comes to it, negotiation snags are either ''formal'' or ''substantive''. ''Formal'' hitches arise when clients challenge terms they don’t ''understand''. ''Substantive'' hitches arise when clients challenge terms they ''do'' understand, because they are ''unreasonable''. | |||
Both scenarios are likely; often at once: if, as tends to be the case, people in your ''own'' organisation don’t understand your documents, it is a bit rich expecting your clients to.<ref>Best example is the [[hypothetical broker dealer]] valuation terms in a [[synthetic equity swap]]. The JC, once responsible for legal coverage of a synthetic equity business, asked what the hell these terms, which were gumming up every single negotiation, were for. No-one knew: all kinds of contradictory ''hypotheses'' were offered by [[tax]] advisors, [[Compliance professional|compliance]] and [[Credit risk|risk officers]] and [[operations]] personnel, but they converged on the simple idea: ''everyone else in the market has this concept in their docs''. </ref> | |||
If your walk away points are genuinely at a point the market will not accept, you do not have a business. Presuming you ''do'' have a business, assume any line drawn ''behind'' the front line is for [[Pantomime dromedary|pantomime]] purposes only. It ''must'' be a false floor. Allow a little gentle pressure on [[senior relationship management]], and it will turn out to be. | |||
That being the case the answer to formal and substantive hitches lies not in playbooks, systems and controls or organisational heft, but in improving product [[design]] and [[user experience]]. | |||
''Make your documents better''. Stop wasting everyone’s time — including your own — with ''pantomimes.'' | |||
===Simplify=== | ===Simplify=== | ||
For | For misunderstood documents, the answer is straightforward, but difficult: ''simplify'' them. This is usually not just a matter of language, but logical structure — though simplifying language often illuminates convoluted logical structures too. Pay attention to [[semantic structure]]. | ||
And, while financial markets drafting is famously dreadful, emerging technologies can help: run your templates through a GPT-3 engine | And, while financial markets drafting is famously dreadful, emerging technologies can help: run your templates through a [[GPT-3]] engine to simplify them. It won’t be perfect and will make errors, but ''it is free''. Error-checking and quality control is what your SMEs are for. Technology can break the back of an otherwise impossible job. | ||
===Remove false floors=== | ===Remove false floors=== | ||
If you know you will settle at ''at least'' ''Z'', then | If you know you will settle at ''at least'' ''Z'', then ''don’t start at X''. | ||
Assuming the goal is to transact, your role is to get to [[Consensus ad idem|“yes”]] as fast as possible. That’s it. | |||
There are no prizes for style, difficulty or technique in hand-to-hand combat at points ''X'', ''Y'' and ''Z'' if you don’t agree until ''Q''. Identify walk away points and ''start'' with them. | |||
“But the client needs to feel like it has ''won'' something”. | |||
You will hear this a lot. It is a self-serving justification for deliberately starting at a place clients won’t like because it keeps people in a job. Invite anyone saying this to give concrete examples where this worked as a strategy, where going straight to the final position would not have. Why deliberately aggravate your clients, adopting an unreasonable position, just to [[performative]]ly climb down from it at the first objection? How does ''that'' create a better impression than presenting a clear, coherent and fair document in the first place? | |||
External advisors do like to be seen to achieve something — it helps justify their costs — but only to an extent. They tend these days to be on fixed fees, and will quickly tire of grandstanding on points they know you will not move on. If they think you will move, on the other hand, they will happily grandstand. Who doesn’t like a bit of pantomime when you get to win it! Therefore, standing ground is a good tactic. It sends a clear message. | |||
===Legaltech as enabler of sloppy thinking=== | |||
Here is a direct quote from a [[legaltech start-up conference|LegalTech start-up conference]] pitch: | |||
{{Quote|“We love automation. We love automating complex things. Our app can handle anything with its structured questions: it can add new clauses, new schedules. The complexity is mind-bending.”}} | |||
Here is where [[Legaltech|LegalTech]]’s great promise confounds us. Legaltech can accommodate any complication we can be bothered to dream up, as if that is a good thing. It offers the capacity ''to do tedious jobs faster''. It allows more variability, optionality and complication within your standard forms. | |||
But this gets the imperative exactly backward. ''You do not want '''more''' complication in your standard forms. You want '''less'''. You want your contracts to all to be the same.'' | |||
Embrace complication not because you can, but ''because you have no other choice''. When you are [[Design|designing]] [[user experience]] for process that is meant to be standard across your platform you absolutely ''do'' have another choice. | |||
{{sa}} | {{sa}} | ||
*[[Process]] | *[[Process]] | ||
*[[Tedium]] | |||
*[[Escalation]] | *[[Escalation]] | ||
*[[Control function]] | *[[Control function]] | ||
| Line 88: | Line 101: | ||
{{ref}} | {{ref}} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:39, 5 December 2023
|
Negotiation Anatomy™
|
“Make your documents better. Stop wasting everyone’s time — including your own — with pantomimes.”
Playbook
/ˈpleɪbʊk/ (n.)
A comprehensive set of guidelines, policies, rules and fall-backs for the legal and credit terms of a contract that you can hand to the itinerant school-leaver from Bucharest to whom you have off-shored your master agreement negotiations.
She will need it because otherwise she won’t have the first clue what do to should customers object, as they certainly will, to the preposterous terms your risk team has insisted go in the first draft of your contracts.
A well-formed playbook ought, therefore, to be like assembly instructions for an Ikea bookshelf.
But Ikea bookshelves do not answer back.
Triage
As far as they go, playbooks speak to the belief that the main risk lies in not following the rules.
They are of a piece with the doctrine of precedent: go, until you run out of road, then stop and appeal to a higher authority. By triaging the onboarding process into “a large, easy, boring bit” — which, in most cases, will be all of it — and “a small, difficult, interesting bit”, playbooks aspire to “solve” that large, easy, boring bit by handing it off to a school-leaver from Bucharest.
Doing large, easy, boring things should not, Q.E.D., need an expensive expert: just someone who is not easily bored, can competently follow instructions and, if she runs out, knows who to ask. She thus tends tilled, tended and fenced land: boundaries have been drawn, tolerances set, parameters fixed, risks codified and processes fully understood. Our children may safely gambol in these fields, where nothing perfidious can befall them.
Escalation
Playbooks maximise efficiency when operating within a fully understood environment. None will ever say, “if the customer does not agree, do what you think is best.” Instead, they will say things like, “any deviations must be escalated for approval by litigation and/or a Credit officer of at least C3 rank”,
The idea is to set up a positive feedback loop such that, through anecdotal escalation, concerned risk control groups can further develop the playbook to keep up with the times and deal with novel situations, the same way the common law courts have done since time immemorial. The playbook is a living document.[1]
In practice, this does not happen because no-one has any time or patience for playbooks.
Example
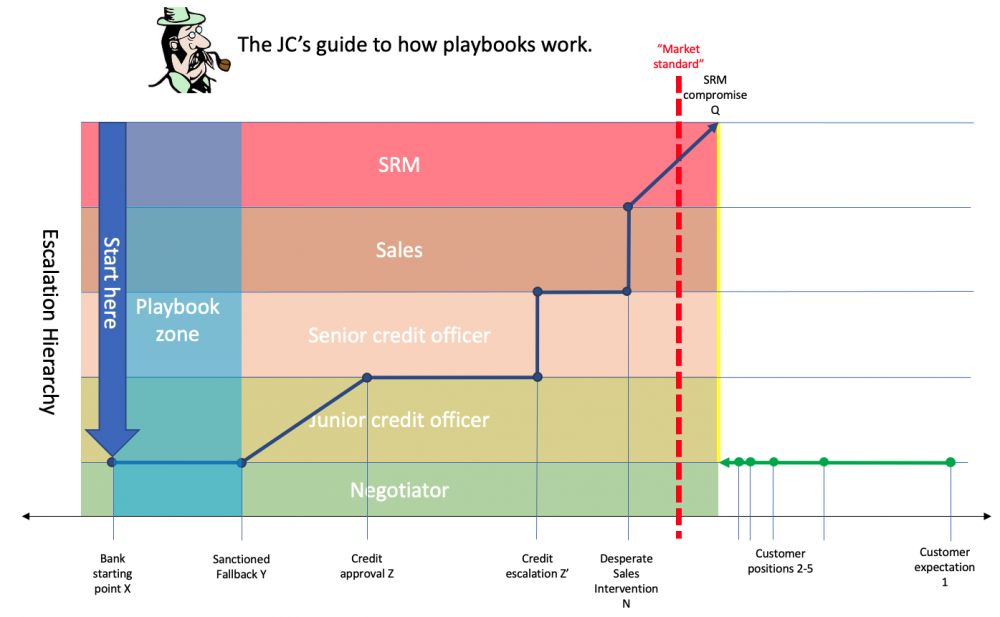
For example, illustrated in the panel above:
- A playbook stipulates starting position X, but allows that if a customer of type B does not agree to X, a satisfactory compromise may be found at Y.
- The playbook “empowers” the negotiator to offer Y — some way yet from any sort of reasonable market standard — without further permission.
- Should customer B not agree to Y, there must be an escalation, to a junior risk officer, who may sanction a further derogation to Z — still unnecessarily conservative, but no longer laugh-out loud preposterous. The negotiator trots back to the customer with Z.
- Should customer not accept Z either, there will follow an extended firefight between risk personnel from either organisation — conducted through their uncomprehending negotiation personnel — taking the negotiation through Z', which will culminate with escalation to sales who might optimistically suggest N, and if that doesn’t do the trick, senior relationship management will be wheeled in, and will cave instantly to the client’s demand to reach a craven surrender at position Q, some way past the market standard and anything remotely necessary or reasonable.
By codifying this process, so the argument goes, not only may we engage materially cheaper negotiation personnel, but we can triage our clients and improve our systems and controls.
But really.
Design and user experience
We have certainly added to our systems and controls; no doubt about that.
But only positions X through Y are codified in the playbook. All those wonderful systems and controls were in play only between X and Y which turned out, quelle surprise, to be a mile behind the front line.
No doubt middle-management can regale its superiors with assorted Gantt charts, dashboards and verdant traffic lights attesting to how well the documentation unit is operating. But all these gears are engaged, and all the systems and controls are running, over the easy, boring bit of the process.
And, at a cost: following this byzantine process to gather this data occupies people and takes time: all negotiations take longer, and none of these gears, rules and triage are engaged at any point where the data might be interesting: the exceptions.
The conundrum: since we know our walk-away position is Z (and, at a push, Q) why are we starting at X? Why is there a fall-back to Y?
Why mechanise an area of the battlefield behind your opponent’s lines, which you know you have no realistic expectation of occupying?
Form and substance
When it comes to it, negotiation snags are either formal or substantive. Formal hitches arise when clients challenge terms they don’t understand. Substantive hitches arise when clients challenge terms they do understand, because they are unreasonable.
Both scenarios are likely; often at once: if, as tends to be the case, people in your own organisation don’t understand your documents, it is a bit rich expecting your clients to.[2]
If your walk away points are genuinely at a point the market will not accept, you do not have a business. Presuming you do have a business, assume any line drawn behind the front line is for pantomime purposes only. It must be a false floor. Allow a little gentle pressure on senior relationship management, and it will turn out to be.
That being the case the answer to formal and substantive hitches lies not in playbooks, systems and controls or organisational heft, but in improving product design and user experience.
Make your documents better. Stop wasting everyone’s time — including your own — with pantomimes.
Simplify
For misunderstood documents, the answer is straightforward, but difficult: simplify them. This is usually not just a matter of language, but logical structure — though simplifying language often illuminates convoluted logical structures too. Pay attention to semantic structure.
And, while financial markets drafting is famously dreadful, emerging technologies can help: run your templates through a GPT-3 engine to simplify them. It won’t be perfect and will make errors, but it is free. Error-checking and quality control is what your SMEs are for. Technology can break the back of an otherwise impossible job.
Remove false floors
If you know you will settle at at least Z, then don’t start at X.
Assuming the goal is to transact, your role is to get to “yes” as fast as possible. That’s it.
There are no prizes for style, difficulty or technique in hand-to-hand combat at points X, Y and Z if you don’t agree until Q. Identify walk away points and start with them.
“But the client needs to feel like it has won something”.
You will hear this a lot. It is a self-serving justification for deliberately starting at a place clients won’t like because it keeps people in a job. Invite anyone saying this to give concrete examples where this worked as a strategy, where going straight to the final position would not have. Why deliberately aggravate your clients, adopting an unreasonable position, just to performatively climb down from it at the first objection? How does that create a better impression than presenting a clear, coherent and fair document in the first place?
External advisors do like to be seen to achieve something — it helps justify their costs — but only to an extent. They tend these days to be on fixed fees, and will quickly tire of grandstanding on points they know you will not move on. If they think you will move, on the other hand, they will happily grandstand. Who doesn’t like a bit of pantomime when you get to win it! Therefore, standing ground is a good tactic. It sends a clear message.
Legaltech as enabler of sloppy thinking
Here is a direct quote from a LegalTech start-up conference pitch:
“We love automation. We love automating complex things. Our app can handle anything with its structured questions: it can add new clauses, new schedules. The complexity is mind-bending.”
Here is where LegalTech’s great promise confounds us. Legaltech can accommodate any complication we can be bothered to dream up, as if that is a good thing. It offers the capacity to do tedious jobs faster. It allows more variability, optionality and complication within your standard forms.
But this gets the imperative exactly backward. You do not want more complication in your standard forms. You want less. You want your contracts to all to be the same.
Embrace complication not because you can, but because you have no other choice. When you are designing user experience for process that is meant to be standard across your platform you absolutely do have another choice.
See also
References
- ↑ This rarely happens in practice. Control functions make ad hoc exceptions to the process, do not build them into the playbook as standard rules, meaning that the playbook has a natural sogginess (and therefore inefficiency).
- ↑ Best example is the hypothetical broker dealer valuation terms in a synthetic equity swap. The JC, once responsible for legal coverage of a synthetic equity business, asked what the hell these terms, which were gumming up every single negotiation, were for. No-one knew: all kinds of contradictory hypotheses were offered by tax advisors, compliance and risk officers and operations personnel, but they converged on the simple idea: everyone else in the market has this concept in their docs.