Evolution by natural selection
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The greatest scientific achievement — or not science at all?
Let’s see if this works.
In essence[1] evolutionary theory is that organisms evolve through a mindless, iterative process — an algorithm. Each iteration has three components:
- Variation: Random but minor variations in organisms, which happen through recombination (mixing of parental genes) or mutation (errors in copying genes).
- Selection: Selection of those variations that are best suited to to the prevailing environment — this will happen naturally; those variants that are less suited will, ipso facto, fare worse and eventually die out.
- Heredity: The features conferring fitness tend to be retained and passed on in successive versions of each reproducing organism. This happens through parental combination.
The process is effectively “trial-and-error” or “generate-and-test”: The problem is how best to survive and replicate in the given environment; the “best” solutions for the process continuously generate new trials, test them, discard failures, and keep the successes.
Observations on the evolutionary process
- It is algorithmic: it is suitable in concept for use by a Turing machine.
- It is profoundly stupid: It requires no insight, intelligence or imagination. Also ideal for use by a Turing machine. Therefore:
- No educated guesses based on acquired assumptions about the environment, the prevailing physical laws of the universe etc.
- No retrospective correction of successful variations which, on subsequent adaptations, turn out to be constraints or design flaws.
- It is profoundly wasteful: It requires trial and error, but because it is stupid, it is entirely unsupported by intelligent insight. It cannot hypothesise that variation x will be more successful than variation y, and so opt for variation x;
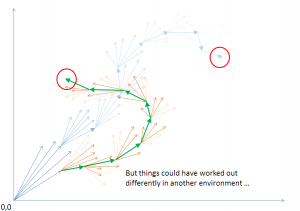
- It is profoundly contingent: what counts as “fitness” depends on a changing environment comprising:
- (a) the organism itself;
- (b) all other (evolving) organisms in the biosphere; and
- (c) changing climate, whether through:
- (i) normal environmental fluctuations (weather, seasonal change, viruses);
- (ii) evolving organisms consuming resources and competing with each other; or
- (iii) extraordinary climactic events (earthquakes, volcanoes, meteorites, invasions of “aliens”).
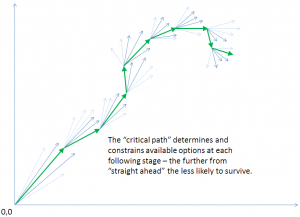
- It is profoundly inefficient: the iterative nature of the evolutionary process is highly unlikely to produce design economy: Each new adaptation depends on, and is layered on top of, all earlier adaptations. The more more recent an adaptation is, the more susceptible it is to successful mutation. Mutations in basic characteristics on which a lot of subsequent bio-engineering depends are likely to be catastrophic. A design flaw that is critical will lead to extinction. A non-critical design-flaw may be that layering work-arounds over earlier design flaws, but there is no mechanism in evolution (other than fiat) to “improve” an underlying design.
- It is path-dependent: Where any step can go depends on where you start and what are the prevailing environmental conditions. The further back down the chain you go,the more divergent subsequent paths can be.
- It is survivor bias writ large
which are taken to be unvarying constants true for all times and all places. Trial and error without theory dependence succeeds only by serendipity and thus depends on largely inexhaustible resources
See also
Plain English Anatomy™ Noun | Verb | Adjective | Adverb | Preposition | Conjunction | Latin | Germany | Flannel | Legal triplicate | Nominalisation | Murder your darlings