Normal distribution: Difference between revisions
Amwelladmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Amwelladmin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
{{Quote|“[Waymo] staff lamented that they have got 99 or cent of the way there but ‘the last 1 per cent’ — the hump that Full Self-Driving will need to get over to live up to its name — has proved hugely complex.” | {{Quote|“[Waymo] staff lamented that they have got 99 or cent of the way there but ‘the last 1 per cent’ — the hump that Full Self-Driving will need to get over to live up to its name — has proved hugely complex.” | ||
:—“Gimmicky Musk hits the skids”, ''The Sunday Times'', 22 August 2021}} | :—“Gimmicky Musk hits the skids”, ''The Sunday Times'', 22 August 2021}} | ||
Then there are those “[[ten sigma event|ten-sigma” events]] — like, ooooh, say the correlation of a Russian government default with a spike in the price of all other G20 Treasury securities, just to pick something at random — that should, in the world of normal distributions, happen only once in every 10<sup>24</sup> times — say, ten million years — but, since investment decisions are not even remotely independent events, happened | Then there are those “[[ten sigma event|ten-sigma” events]] — like, ooooh, say the correlation of a Russian government default with a spike in the price of all other G20 Treasury securities, just to pick something at random — that should, in the world of normal distributions, happen only once in every 10<sup>24</sup> times — say, ten million years — but, since investment decisions are not even remotely independent events, happened once — and only needed to happen once, to blow [[Long Term Capital Management]] and much of the market to smithereens — in ''four'' years. | ||
These persist in occurring “against all odds” because they are a product of ''dependent'' events. The distribution of patrons’ arrival times at a cinema are normally distributed around the prescribed showtime because, outside that control, the time at which ''I'' show up has no bearing, or dependency, on the time [[Mrs Pinterman]] shows up. The chance that all 400 people should arrive and try to enter the theatre at the same moment is more or less nil. | These persist in occurring “against all odds” because they are a product of ''dependent'' events. The distribution of patrons’ arrival times at a cinema are normally distributed around the prescribed showtime because, outside that control, the time at which ''I'' show up has no bearing, or dependency, on the time [[Mrs Pinterman]] shows up. The chance that all 400 people should arrive and try to enter the theatre at the same moment is more or less nil. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
When assessing probabilities, therefore, pay attention to the dependency of the events. If events are interdependent, ''[[normal]] distributions to not apply. | When assessing probabilities, therefore, pay attention to the dependency of the events. If events are interdependent, ''[[normal]] distributions to not apply. | ||
This seems an obvious lesson; the JC feels less patronising about stating it since failure to heed it led to the collapse of [[LTCM]] ''and'' the [[global financial crisis]]. | This seems an obvious lesson; the JC feels less patronising about stating it since failure to heed it led to the collapse of [[LTCM]] ''and'' the [[global financial crisis]]. This from someone who really should have known better: | ||
{{Quote|“We were seeing things that were 25-standard deviation moves, several days in a row.” | {{Quote|“We were seeing things that were 25-standard deviation moves, several days in a row.” | ||
:—David Viniar, Chief Financial Officer, [[Goldman]]}} | :—David Viniar, Chief Financial Officer, [[Goldman]]}} | ||
The probability of a 25 standard deviation move is 1.309 x 10 ^ 130. You see this figure cited frequently, but to a lay person, it doesn't really make the same impact as writing it out, so let's to that. | ''Twenty five'' standard deviations. That makes LTCM seem like a near certainty. The probability of a 25 standard deviation move<ref>Good [https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/business/who-we-are/centres-and-institutes/gcbfi/documents/cris-reports/cris-paper-2008-3.pdf paper on this from Nottingham University].</ref> is 1.309 x 10 ^ 130. You see this figure cited frequently, but to a lay person, it doesn't really make the same impact as writing it out, so let's to that. | ||
{{Quote|1 day in 1.3 billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion days. | {{Quote|1 day in 1.3 billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion days. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
By comparison, the earth is 1658 billion days old, and the universe itself ten times older than that. So we are talking about an event that you would only expect once in several billion billion billion billion billion lives of the universe, happening ''several days in a row''. | By comparison, the earth is 1658 billion days old, and the universe itself ten times older than that. So we are talking about an event that you would only expect once in several billion billion billion billion billion lives of the universe, happening ''several days in a row''. | ||
No, Mr Viniar: you weren’t seeing cosmologically-defying anomalies. ''Your models were wrong''. But enough already of the chutzpah.<ref>But, [[get your coat]], you know?</ref> The practical lesson is that, unless you are dealing with normally-distributed events, normal probabilities are a ''really'' bad proxy at the extremes. ''Ninety-nine per cent of the way there is nowhere. It isn’t good enough''. | |||
''All'' existential crises sit in the last 1 per cent — last 0.01 per cent, even — because the defining feature of an existential crisis is ''everyone panicking and selling at once''. These are, by definition, the events a normal distribution says will not happen, because events in a normal distribution are independent of each other. | |||
The allure of the normal distribution is that you can calculate it, it’s easy to use, and inside those extremes — where people aren’t panicking, stampeding for theatre exits, selling all at once, hanging off transporter plane fuselage — events though not independent, look near enough like they could be. Variations cancel each other out. Bulls offset bears. So, the temptation is to use normal distributions to model risk:<ref>The [[Black-Scholes option pricing model]] is for example.</ref> ninety-nine percent of the time, they work fine. But it’s the ninety-nine per cent of the time you don't really ''need'' your risk model. | The allure of the normal distribution is that you can calculate it, it’s easy to use, and inside those extremes — where people aren’t panicking, stampeding for theatre exits, selling all at once, hanging off transporter plane fuselage — events though not independent, look near enough like they could be. Variations cancel each other out. Bulls offset bears. So, the temptation is to use normal distributions to model risk:<ref>The [[Black-Scholes option pricing model]] is for example.</ref> ninety-nine percent of the time, they work fine. But it’s the ninety-nine per cent of the time you don't really ''need'' your risk model. | ||
===Interdependent = [[complex]]=== | |||
The thing about interdependent events is not that it’s ''hard'' to predict them: it is ''impossible''. These are [[complex]], [[non-linear]] interactions between parts of a [[System|distributed system]] that no-one is watching with an eye to the particular scenario. You can control these only if you can switch the system off without consequence as soon as an unexpected event happens. With ungoverned, tightly-coupled, organic, distributed systems comprising autonomous components with imperfect information, you cannot just switch the system off. | |||
{{sa}} | {{sa}} | ||
*[[ | *[[Normal accidents]] | ||
*[[Archegos]] | |||
*[[Black-Scholes option pricing model]] | |||
{{ref}} | |||
Revision as of 11:00, 22 August 2021
|
|
A Gaussian, or normal distribution of a series of events, indicates that the events are independent of each other, in that the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of another. Coin flips are independent of each other. So are rolls of a die, or the distribution of heights in a classroom. Homo sapiens being the fickle, biddable species it is, its cognitive decisions — particularly those concerning fashionable ideas, to depart quickly from crowded theatres when someone yells fire or to hysterically buy, and then sell, Enron stock for fear of missing out — are not.
Independent events
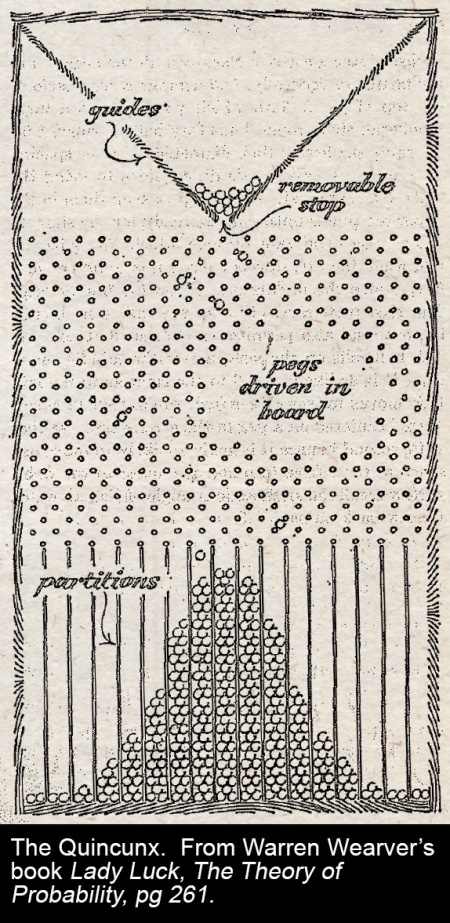
Independent events fit nicely to a bell curve, as the quincunx pictured, likes to demonstrate. Bell curves confidently prescribe standard deviations, probability intervals, and allow one the comfort to say, “the odds of x are such that one wouldn’t expect it in several lives of the universe”. When x really is an independent event (or a series of them) this is prudent enough: “the odds of flipping a coin and getting 99 consecutive heads is 0.5 x 1099, which you wouldn’t expect in several lifetimes of the universe.”
Dependent events
“[Waymo] staff lamented that they have got 99 or cent of the way there but ‘the last 1 per cent’ — the hump that Full Self-Driving will need to get over to live up to its name — has proved hugely complex.”
- —“Gimmicky Musk hits the skids”, The Sunday Times, 22 August 2021
Then there are those “ten-sigma” events — like, ooooh, say the correlation of a Russian government default with a spike in the price of all other G20 Treasury securities, just to pick something at random — that should, in the world of normal distributions, happen only once in every 1024 times — say, ten million years — but, since investment decisions are not even remotely independent events, happened once — and only needed to happen once, to blow Long Term Capital Management and much of the market to smithereens — in four years.
These persist in occurring “against all odds” because they are a product of dependent events. The distribution of patrons’ arrival times at a cinema are normally distributed around the prescribed showtime because, outside that control, the time at which I show up has no bearing, or dependency, on the time Mrs Pinterman shows up. The chance that all 400 people should arrive and try to enter the theatre at the same moment is more or less nil.
But when Mrs. Pinterman then cries “fire” the situational dynamic is very different. Everyone tries to leave at once. Even those who didn't hear Mrs. Pinterman directly, because they instinctively copy everyone else,who did.
When assessing probabilities, therefore, pay attention to the dependency of the events. If events are interdependent, normal distributions to not apply.
This seems an obvious lesson; the JC feels less patronising about stating it since failure to heed it led to the collapse of LTCM and the global financial crisis. This from someone who really should have known better:
“We were seeing things that were 25-standard deviation moves, several days in a row.”
- —David Viniar, Chief Financial Officer, Goldman
Twenty five standard deviations. That makes LTCM seem like a near certainty. The probability of a 25 standard deviation move[1] is 1.309 x 10 ^ 130. You see this figure cited frequently, but to a lay person, it doesn't really make the same impact as writing it out, so let's to that.
1 day in 1.3 billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion billion days.
or
1 day in 1300000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 days.
By comparison, the earth is 1658 billion days old, and the universe itself ten times older than that. So we are talking about an event that you would only expect once in several billion billion billion billion billion lives of the universe, happening several days in a row.
No, Mr Viniar: you weren’t seeing cosmologically-defying anomalies. Your models were wrong. But enough already of the chutzpah.[2] The practical lesson is that, unless you are dealing with normally-distributed events, normal probabilities are a really bad proxy at the extremes. Ninety-nine per cent of the way there is nowhere. It isn’t good enough.
All existential crises sit in the last 1 per cent — last 0.01 per cent, even — because the defining feature of an existential crisis is everyone panicking and selling at once. These are, by definition, the events a normal distribution says will not happen, because events in a normal distribution are independent of each other.
The allure of the normal distribution is that you can calculate it, it’s easy to use, and inside those extremes — where people aren’t panicking, stampeding for theatre exits, selling all at once, hanging off transporter plane fuselage — events though not independent, look near enough like they could be. Variations cancel each other out. Bulls offset bears. So, the temptation is to use normal distributions to model risk:[3] ninety-nine percent of the time, they work fine. But it’s the ninety-nine per cent of the time you don't really need your risk model.
Interdependent = complex
The thing about interdependent events is not that it’s hard to predict them: it is impossible. These are complex, non-linear interactions between parts of a distributed system that no-one is watching with an eye to the particular scenario. You can control these only if you can switch the system off without consequence as soon as an unexpected event happens. With ungoverned, tightly-coupled, organic, distributed systems comprising autonomous components with imperfect information, you cannot just switch the system off.
See also
References
- ↑ Good paper on this from Nottingham University.
- ↑ But, get your coat, you know?
- ↑ The Black-Scholes option pricing model is for example.